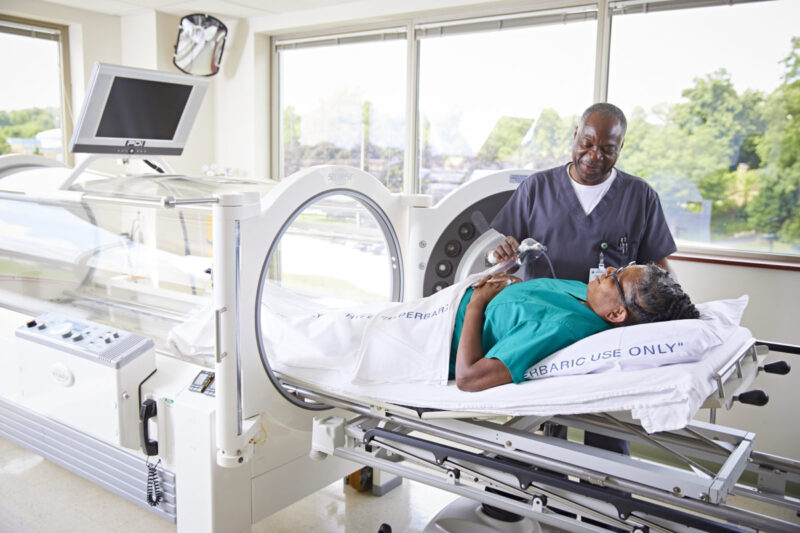
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) chambers are an intriguing blend of medical innovation and therapeutic techniques. This article discusses the intricate world of HBOT chambers, exploring their functionality, applications, and providing practical tips for users.
The goal is to offer a clear, informative, and engaging insight into HBOT chambers, making this complex subject approachable and comprehensible to a wide audience.
Page Contents
The Essence of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
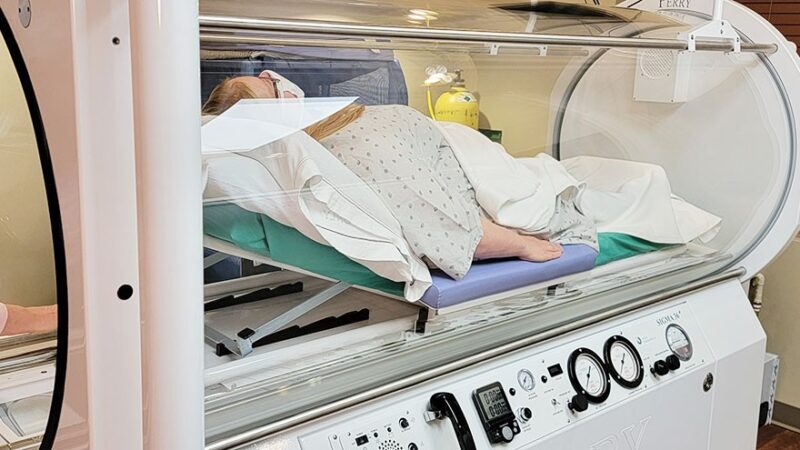
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment involving the inhalation of pure oxygen in a pressurized environment.
This procedure is carried out in an HBOT chamber, a specialized medical device. It significantly increases atmospheric pressure, allowing the body to absorb more oxygen than would be possible at normal air pressure.
For those interested in exploring the benefits of HBOT in the comfort of their own home, HBOT at home offers state-of-the-art hyperbaric chambers tailored for personal use, ensuring safety, convenience, and effectiveness.
The History and Evolution
The concept of pressurized treatment dates back to the 17th century, but modern HBOT chambers have evolved considerably since.
Initially used for treating decompression sickness in divers, their application has broadened over the years. Today’s chambers range from small, portable units to large, hospital-based facilities.
Types of Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers
There are two primary types of HBOT chambers: monoplace and multiplace. Monoplace chambers are designed for a single person, where the individual is enclosed in a tube-like structure.
In contrast, multiplace chambers can accommodate multiple patients simultaneously, with a medical attendant usually present inside to monitor and assist.
How HBOT Chambers Work
The underlying principle of HBOT is Henry’s Law, which states that the amount of gas dissolved in a liquid is proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
In the context of HBOT, when the body is exposed to high-pressure oxygen, more oxygen gets dissolved in the blood plasma, leading to increased oxygen delivery to tissues.
The Role of Increased Atmospheric Pressure
The increased atmospheric pressure in an HBOT chamber (typically about 1.5 to 3 times the normal atmospheric pressure) plays a crucial role.
It helps in dissolving more oxygen into the bloodstream, which can aid in faster healing of damaged tissues and improved infection control.
Oxygen Distribution in the Body
Under these conditions, oxygen is not only carried by red blood cells but also dissolved in the blood plasma.
This allows higher oxygen levels to reach areas in the body where circulation is diminished or blocked, promoting healing in hard-to-reach tissues.
Medical Applications
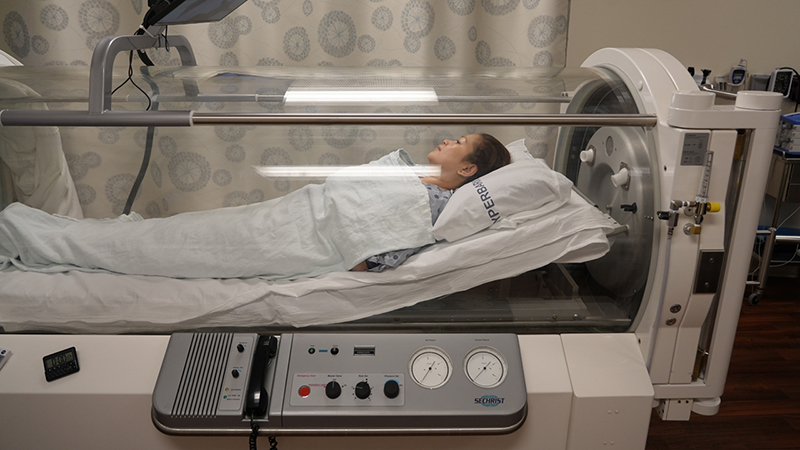

Treating Decompression Sickness
Decompression sickness, also known as ‘the bends’, primarily affects divers. HBOT is the standard treatment for this condition as it helps reduce the bubbles of gas that form in the body during rapid ascents.
Wound Healing and Infection Control
HBOT is beneficial in accelerating wound healing, especially in cases of diabetic foot ulcers, radiation injuries, and infections where blood supply is compromised. The high levels of oxygen can enhance tissue repair and fight infection-causing bacteria.
Neurological and Other Applications
Emerging research suggests potential benefits in neurological conditions like stroke, traumatic brain injury, and multiple sclerosis. However, these applications are still under investigation, and HBOT is not universally accepted for these conditions.
Practical Tips
Before the Session
- Medical Consultation: Consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing HBOT. It’s essential to discuss your medical history and current health conditions.
- Understanding the Process: Familiarize yourself with the procedure to reduce anxiety and increase comfort during the session.
During the Session
- Communication: In a multiplace chamber, a technician will be present inside, with whom you can communicate. In a monoplace chamber, you’ll typically be in visual contact with an operator outside the chamber.
- Managing Discomfort: You may experience pressure in your ears similar to ascending in an airplane. Techniques like swallowing or yawning can help equalize ear pressure.
After the Session
- Monitoring Reactions: Although rare, some people might experience fatigue or light-headedness post-session. It’s vital to report any adverse reactions to the medical team.
- Continued Care: Follow any specific post-treatment instructions given by your healthcare provider.
Navigating Challenges and Safety
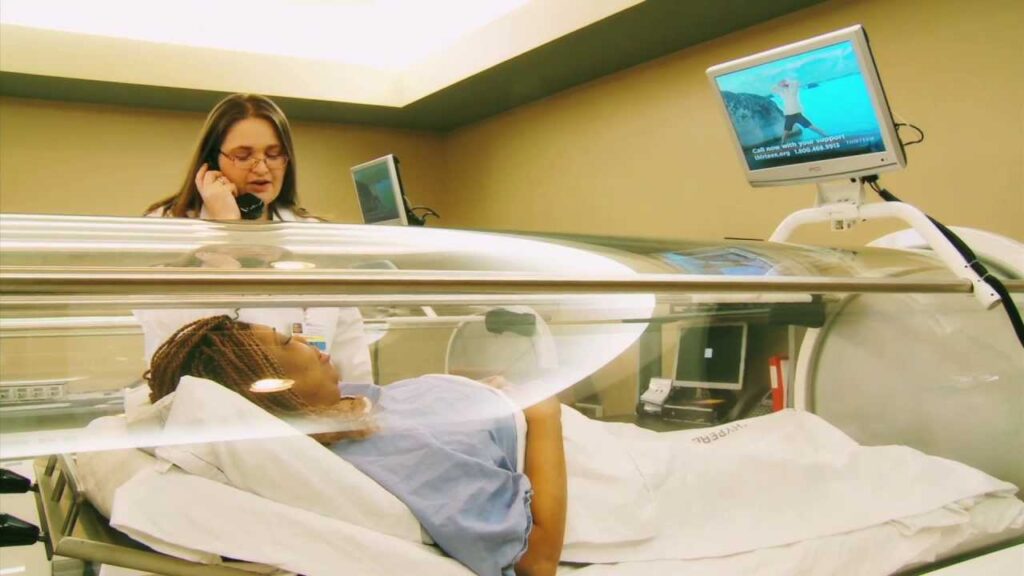

While HBOT is generally safe, it’s not without risks. Potential complications, though rare, can include ear and sinus injuries due to pressure changes, temporary nearsightedness, and, in extreme cases, oxygen toxicity.
It’s crucial to understand that certain conditions, like untreated pneumothorax, are contraindications for HBOT.
Safety Protocols
Safety is paramount in HBOT. Chambers are designed with strict safety guidelines to prevent fire hazards, given the high oxygen environment. It’s essential to follow all instructions regarding clothing, personal items, and behavior inside the chamber.
Emergency Procedures
Both patients and staff should be aware of emergency procedures. This includes knowledge of how to rapidly depressurize the chamber if necessary and the steps to follow in case of a medical emergency during the therapy.
The Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have led to more sophisticated HBOT chambers. Features like improved patient comfort, enhanced safety mechanisms, and better control systems are now standard. Some chambers even offer entertainment systems to help patients relax during treatment.
Portable and Home-Based Chambers
The development of portable and home-based HBOT chambers has made this therapy more accessible. These chambers, while less powerful than traditional models, offer convenience for certain conditions that require frequent or long-term treatment.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is focusing on optimizing HBOT protocols and exploring new therapeutic applications. The future might see HBOT becoming a more integral part of treatments for a broader range of conditions.
Integrating HBOT in Healthcare Regimens
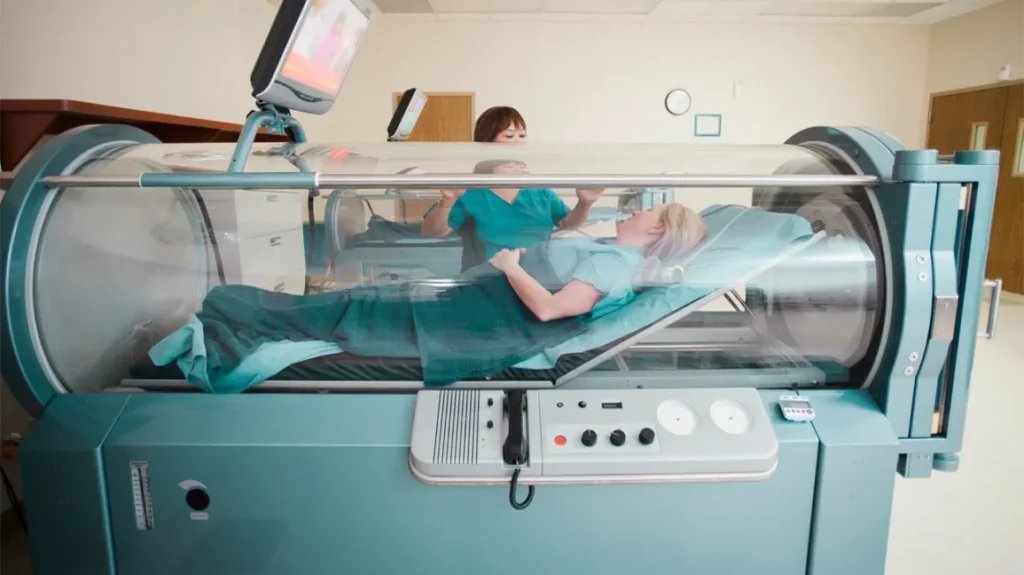
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
HBOT should be part of a coordinated healthcare plan. Patients need to work closely with their healthcare providers to integrate HBOT effectively into their overall treatment strategy.
Insurance and Coverage Considerations
Understanding insurance coverage for HBOT is essential, as not all conditions treated with HBOT are covered by insurance plans. It’s advisable to check with insurance providers and seek clarity on coverage aspects.
Patient Advocacy and Education
Patients should actively seek information and advocate for their care. Being educated about HBOT helps in making informed decisions and discussing potential benefits and risks with healthcare providers.
Concluding Thoughts
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and HBOT chambers present a fascinating intersection of advanced technology and therapeutic treatment.
From treating divers with decompression sickness to aiding in the healing of chronic wounds, HBOT has proven its versatility and effectiveness. As research continues, the potential applications of this therapy may expand further, offering hope and healing in areas of medicine previously thought challenging.
Knowing the workings of HBOT chambers, their medical applications, and the practical tips for their use can demystify this advanced therapy, making it more accessible and comprehensible. Whether for personal knowledge or professional interest, grasping the complexities of HBOT chambers enriches one’s understanding of modern medical marvels.